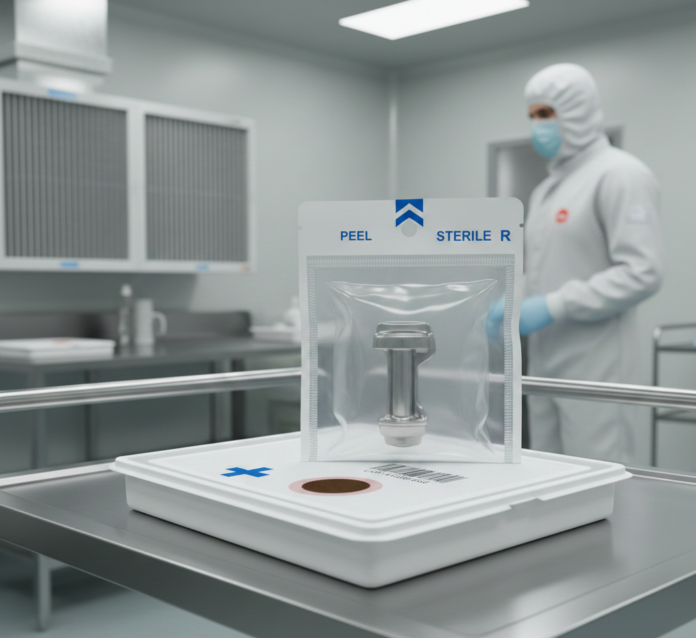
The sterile packaging market encompasses specialized packaging solutions designed to maintain product sterility from manufacturing through storage, transportation, and final use. These solutions play a vital role across healthcare, pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical device industries, where contamination control is essential for patient safety and regulatory compliance.
According to Research Intelo, the global sterile packaging market was valued at US$ 42.1 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach US$ 72.7 billion by 2033, expanding at a CAGR of 6.2%. This steady growth reflects the increasing demand for sterile medical products, expanding pharmaceutical production, and heightened focus on infection prevention worldwide.
Sterile packaging systems are engineered to withstand sterilization processes such as steam, ethylene oxide, radiation, and chemical sterilization while preserving the integrity and functionality of the packaged product. As quality assurance and patient safety continue to dominate healthcare priorities, sterile packaging has become an indispensable component of modern medical infrastructure.
Why Is sterile packaging critical in healthcare and pharmaceuticals?
Sterility is non-negotiable in environments where products come into direct contact with patients or sensitive biological systems. Surgical instruments, implants, syringes, diagnostic kits, and pharmaceutical products all rely on sterile packaging to prevent microbial contamination.
Without appropriate sterile barriers, even advanced medical products can become ineffective or harmful. As healthcare systems globally continue to focus on patient safety, hospital-acquired infection reduction, and stringent quality standards, the demand for reliable sterile packaging solutions continues to rise.
Which materials are commonly used in sterile packaging?
A wide range of materials is employed in sterile packaging, selected based on product compatibility, sterilization method, and regulatory requirements. Key material categories include:
- Plastics: Widely adopted due to versatility, cost efficiency, and strong barrier properties. Materials such as polyethylene, polypropylene, and PET are commonly used in trays, bottles, vials, and pouches, offering effective protection against moisture, oxygen, and external contaminants.
- Paper and Paperboard: Frequently used for wraps, pouches, and blister packs, supported by increasing demand for sustainable packaging solutions. Advances in coated and laminated paper technologies are improving barrier performance and expanding applicability in healthcare and pharmaceutical settings.
- Aluminum Foils: Valued for excellent barrier protection against light, moisture, and gases, particularly in pharmaceutical packaging applications.
- Glass: Preferred for applications requiring high chemical resistance and product visibility, such as injectable drug and vaccine packaging. While glass provides superior inertness and impermeability, brittleness and higher costs present ongoing challenges.
Continuous innovation in material science, coupled with sustainability initiatives, is shaping the evolution of sterile packaging materials.
How do sterilization methods influence packaging design?
Sterilization methods directly influence packaging structure, material selection, and overall system design. Packaging solutions must endure exposure to high temperatures, pressure, radiation, or chemical agents without compromising sterility or functional performance.
Steam sterilization demands heat-resistant materials, while ethylene oxide sterilization requires breathable packaging structures that allow gas penetration and aeration. Radiation sterilization, in contrast, necessitates materials that remain stable without degradation or harmful by-product formation. As sterilization technologies advance, packaging designs are increasingly tailored to ensure both compatibility and operational efficiency.
What role does regulation play in market growth?
Regulatory frameworks play a central role in shaping the sterile packaging market. Government agencies and international organizations enforce stringent quality and safety standards for packaging used in medical and pharmaceutical applications. Compliance with regulations such as ISO 11607 for terminally sterilized medical device packaging and requirements outlined by the US Pharmacopeia is driving manufacturers to invest in advanced materials, validation testing, and process controls.
In parallel, policy reforms and incentives supporting domestic manufacturing of medical and pharmaceutical products in several regions are stimulating demand for compliant sterile packaging solutions that meet global quality benchmarks.
Which end-use industries are driving demand?
The healthcare sector remains the largest consumer of sterile packaging, particularly across hospitals, clinics, and surgical centers. However, sustained growth is also evident in:
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing
- Medical device production
- Biotechnology and life sciences
- Diagnostic and laboratory applications
The rising adoption of minimally invasive procedures, expansion of home healthcare services, and increasing use of point-of-care diagnostics continue to support market expansion across these end-use segments.
How Is sustainability shaping the sterile packaging market?
Sustainability considerations are increasingly influencing packaging strategies, even within highly regulated healthcare environments. Although sterility requirements limit material flexibility, manufacturers are exploring recyclable polymers, lightweight packaging formats, and resource-efficient production processes.
Balancing environmental responsibility with sterility assurance remains a complex challenge. However, advancements in material engineering and lifecycle analysis are enabling gradual progress toward more sustainable sterile packaging solutions.
What does the future hold for the sterile packaging market?
With the global sterile packaging market projected to grow from US$ 42.1 billion in 2024 to US$ 72.7 billion by 2033, continued expansion is expected across both developed and emerging healthcare markets. Key trends shaping the future include automation in packaging operations, enhanced barrier technologies, smart packaging integration, and greater regulatory harmonization across regions.
As healthcare delivery models evolve and pharmaceutical innovation accelerates, sterile packaging will remain a foundational element supporting safety, compliance, and supply chain efficiency.
Why does sterile packaging remain indispensable?
Sterile packaging occupies a critical position at the intersection of safety, science, and regulation. Its role in safeguarding sensitive medical and pharmaceutical products underscores its importance across the global healthcare ecosystem. Supported by steady market growth and ongoing technological advancements, the sterile packaging market is well positioned to meet rising healthcare demands and evolving regulatory expectations in the years ahead.