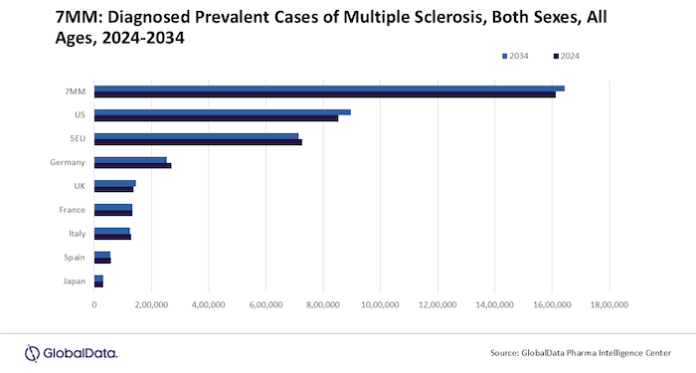
The diagnosed prevalent cases of multiple sclerosis (MS) in the seven major markets (7MM – The US, 5EU (France, Germany, Italy, Spain, the UK), and Japan) are projected to increase from 1.61 million in 2024 to 1.64 million in 2034 at an annual growth rate (AGR) of negative 0.19%, forecasts GlobalData, a leading data and analytics company.
GlobalData’s latest report, “Multiple Sclerosis Epidemiology Analysis and Forecast to 2034,” reveals that in 2034, the US is forecasted to experience the greatest number of diagnosed prevalent cases of MS among the 7MM, totaling 896,828 cases, while Japan is projected to have the lowest count at 31,527 cases.
MS is an autoimmune disease that mainly affects the central nervous system, causing nerve sheath demyelination, followed by axon damage and paralysis. Most people with MS have a relapsing-remitting disease course. MS symptoms may occur and disappear completely, while permanent neurological problems happen when the disease advances.
The diagnosis of MS depends upon the patient’s symptoms, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and laboratory results, but it is mostly diagnosed in the late phases. There are five types of MS, which can be distinguished depending on MS duration and future MS progression, and the distinction is important to determine treatment. Currently, there is no cure for MS. However, treatments can help speed recovery from attacks, modify the course of the disease, and manage symptoms.
Rahul N Ravi, MPH, senior epidemiologist at GlobalData, comments: “In 2024, adults ages 50–59 years accounted for the highest proportion of the diagnosed prevalent cases of MS in the 7MM. This age distribution aligns with findings that show higher MS prevalence among middle-aged populations.”
MS is the most common progressive disease of the central nervous system in young adults and the most common cause of serious physical disability in adults of working age. It is pathologically characterized by focal areas of inflammation, demyelination, gliosis, and axonal damage throughout the central nervous system. The course of MS is characterized by clinical relapses and disease progression.
Ravi concludes: “Early diagnosis of MS has increased over the past few decades. The availability of neurologists and diagnostic tools has a strong link to MS diagnosis. Also, there is an increased awareness of MS in both the public and clinical communities.
“Over the past 30 years, the increase in the women-to-men sex ratio strongly indicates the existence of an environmental influence on the risk of MS. These observations should prompt epidemiological studies to focus on factors in the Western female lifestyle that have changed over recent decades.”