South Korea is one of the few countries that has managed to contain Covid-19 pandemic without imposing any serious domestic and international mobility restrictions. This has been made possible with the use of technology for extensive testing, contact tracing, and sharing essential information, according to GlobalData.
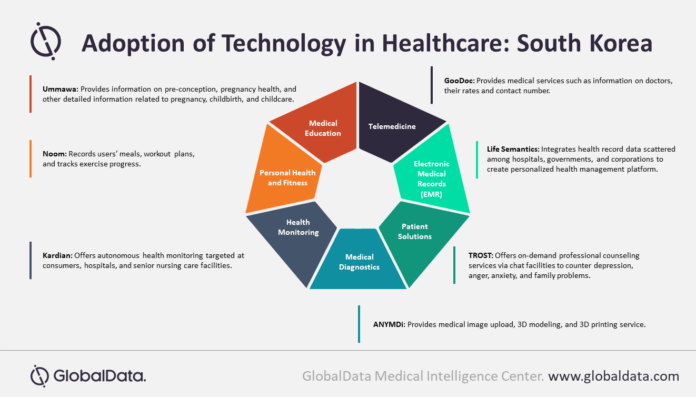
GlobalData’s report, ‘CountryFocus: Healthcare, Regulatory and Reimbursement Landscape – South Korea’, reveals that the South Korean digital healthcare market, which was US$2.9 billion (approximately 21,000 crore) in 2015, is expected to reach US$ 5.4 billion (approximately Rs 40,000 crore) by the end of 2020. The Covid-19 pandemic has led to the relaxation of telemedicine regulations by the South Korean government, opening up the sector for investment and other digital health sectors.
With experience in dealing with the MERS outbreak in 2015, South Korea was prepared for similar outbreaks. The government took measures such as adding public disclosure provisions to the Infectious Disease Control and Prevention Act and permitting laboratories to use unauthorized in-vitro diagnostic kits in a public health emergency.
South Korea collected transaction data even before the outbreak and the nation repurposed the information from cellular GPS data, credit card transactions, drug purchase records, and CCTV footage to track infected people and their movement, days before they got infected.
Tathagata Ghosh, Medical Devices analyst at GlobalData, comments, “The government informs people of any new cases in their districts almost immediately through their cellphones. This way anyone who suspects to have crossed paths with a patient can immediately get tested. The success of this method was instrumental in the recovery of 10,868 of the 12,421 confirmed cases by June end and helped raise the confidence of people in digital health, paving the way for future investment.”
According to GlobalData, a total of 111 health tech deals worth about US$ 2.8 billion (approximately Rs 20,000 crore) were executed between 2019 and H1 2020. South Korea aims to lead the post-Covid-19 era by transforming itself into a digital economy. It is pursuing the ‘Digital New Deal’, which aims to extensively digitize the national infrastructure by promoting 5G technology, big data, artificial intelligence, and non-contact industries.
Ghosh concludes, “The success of digital health in controlling the Covid-19 pandemic in South Korea resulted in increased interest and investment in the digital health sector. With investments of approximately US$ 2.2 billion (approximately Rs 16,000 crore) in the ‘Digital New Deal’ and potential future investments, South Korea aims to revive its economy in the post-Covid-19 world.”